Best Melasma Treatment: Dermatologist-Recommended Solutions
- Home
- Skin rejuvenation
- is there any treatment for melasma

Dermatologists typically recommend a combination therapy of topical agents like hydroquinone, azelaic acid, and tretinoin alongside procedures such as chemical peels, laser therapy, and microdermabrasion for treating Melasma. Utilizing broad-spectrum sunscreens with SPF 30 or higher is essential to protect against UV radiation, which exacerbates the condition. Treatments should be tailored based on individual skin type and pigmentation severity for best results. Continued professional consultation will guarantee the regime is adapted as necessary for long-term management.
What is Melasma, and How is it Diagnosed?
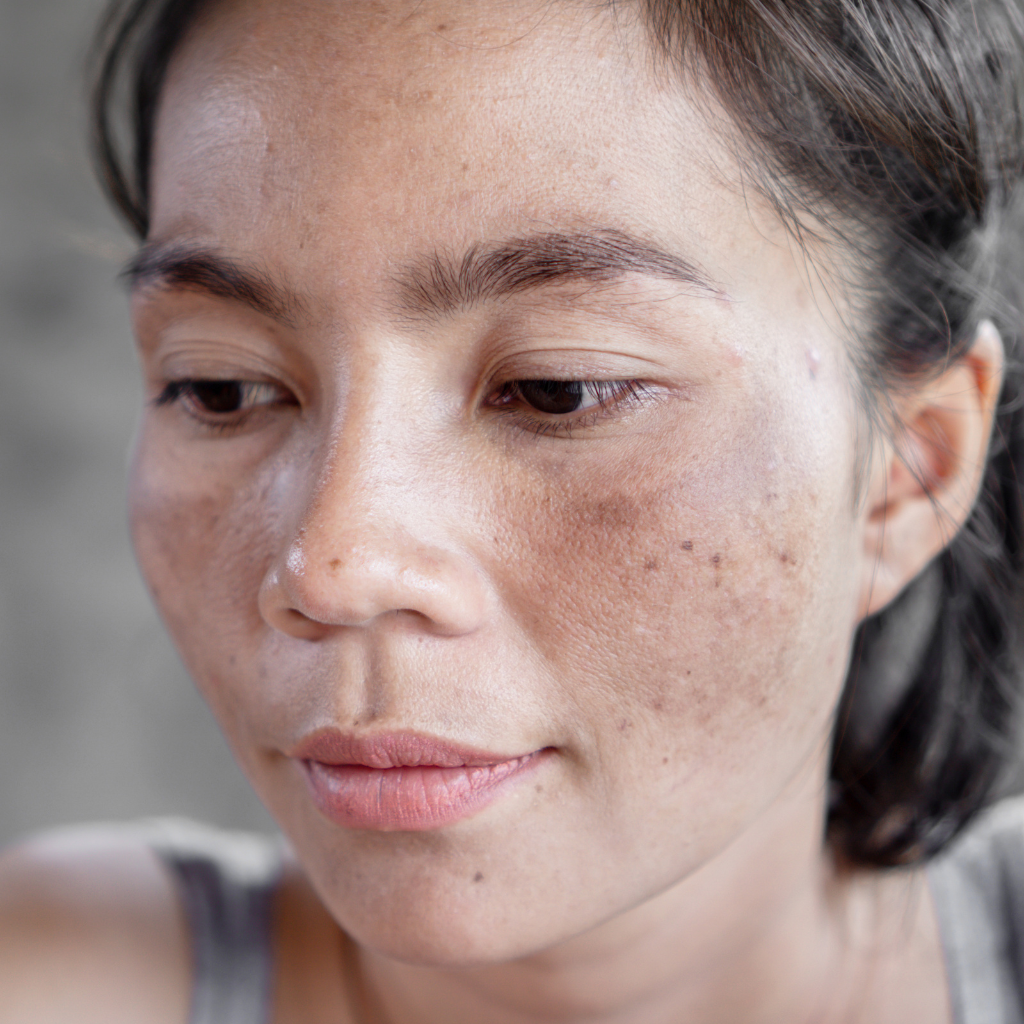
Melasma, a prevalent skin condition, manifests as irregular patches of hyperpigmentation primarily on sun-exposed areas of the skin, affecting women more frequently than men.
The etiology of Melasma is multifactorial, with hormonal fluctuations and UV radiation being significant contributors.
Diagnosis typically involves a clinical examination and may be confirmed using a Wood’s lamp, which highlights the extent of pigmentation changes more clearly.
Understanding Melasma: A Common Skin Condition
Characterized by dark, irregular patches on the skin, this condition, commonly known as Melasma, primarily affects women and is particularly prevalent among those of reproductive age.
Melasma is a skin condition marked by excess pigment, leading to a noticeable discoloration that can affect the overall skin tone. This hyperpigmentation is more common in darker skin tones, where the contrast can be more pronounced.
Diagnosing Melasma typically involves a visual examination by a dermatologist, who assesses the pattern and distribution of the skin discoloration.
Topical treatments to reduce pigmentation are often the first line of defense in treating Melasma. These topical medications include ingredients that inhibit pigment production and are enhanced by minimizing sun exposure to prevent further pigmentation.
Causes of Melasma: Hormonal and Environmental Factors
Understanding the underlying causes of Melasma is key to developing effective treatment plans. Hormonal factors play a significant role, particularly in pregnant women and those using oral contraceptives like birth control pills, which influence melanin production through estrogen receptors. Environmental factors, such as straightforward sun exposure, exacerbate Melasma, making sun protection critical.
Factor Type | Examples | Impact on Melasma |
Hormonal | Pregnancy, Oral contraceptives | Increases melanin synthesis |
Environmental | UV exposure | Triggers pigment production |
Protective Measures | Broad spectrum sunscreen, Oral tranexamic acid | Reduces & prevents severity |
These insights emphasize the importance of a tailored approach, integrating both prevention through broad-spectrum sunscreens and innovative treatments like oral tranexamic acid for managing this complex condition.
What are the Best Treatment Options for Melasma?
Identifying the most effective treatments for Melasma is essential for managing this complex skin condition.
Topical creams, often the first line of treatment, vary in ingredients and efficacy, requiring careful selection based on individual patient needs.
Additionally, procedural interventions such as chemical peels, laser therapies, and Intense pulsed-light therapy (IPL) offer varying degrees of success, with considerations for skin type and color playing a pivotal role in their safety and effectiveness.
Topical Creams and Their Effectiveness for Melasma Patients
While numerous treatments are available for Melasma, topical creams remain a cornerstone of management due to their targeted approach and proven efficacy.
Topical therapy, mainly using medications such as azelaic acid, kojic acid, and tranexamic acid, focuses on reducing the production and deposition of dermal pigment by interfering with the melanin synthesis pathways of pigment cells.
Azelaic acid is known for its ability to gently interrupt pigment production, whereas kojic acid serves as a depigmenting agent by inhibiting tyrosinase, an essential enzyme in melanin production.
Tranexamic acid, less commonly used, helps by minimizing UV-induced pigmentation. Topical corticosteroids may be added to reduce inflammation and skin irritation.
The triple combination cream, blending multiple depigmenting agents, often shows superior results by addressing hyperpigmentation through multiple mechanisms.
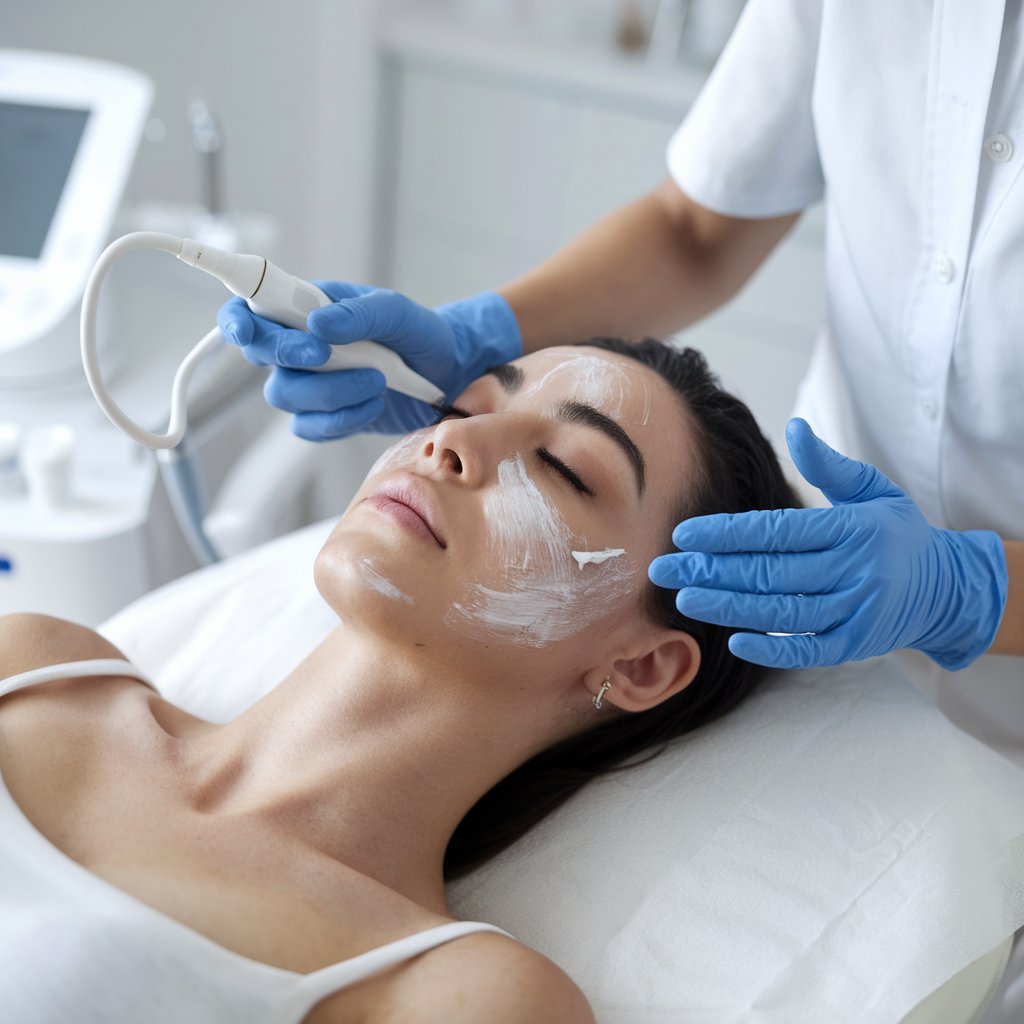
The Role of Chemical Peels in Treating Melasma
Beyond topical creams, chemical peels emerge as another effective strategy for managing Melasma, particularly for patients seeking alternatives or adjunctive treatments.
These peels typically utilize glycolic acid or lactic acid to exfoliate the skin’s superficial layer, where excessive pigment production contributes to Melasma. By removing these outer layers, chemical peels can reduce the visibility of hyperpigmented patches, offering a more transparent and even complexion.
Moreover, when combined therapy is used, chemical peels enhance the overall effectiveness of melasma treatment. They help in minimizing the risk of post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation, a common concern with more invasive procedures.
As treatment options expand, chemical peels remain a preferred choice for their balance of efficacy and safety in managing the aesthetic challenges of Melasma.
Exploring Laser Treatments: Are They Safe for Darker Skin Tones?
Are laser treatments safe for individuals with darker skin tones seeking relief from Melasma? The use of laser therapy in managing Melasma among dark-skinned patients requires careful deliberation due to the potential for hyperpigmentation and scarring.
Here’s what to reflect on:
- Q-Switched Lasers: These are often recommended as they are designed to target melanin selectively with minimal heat damage to surrounding tissues.
- Laser Treatment Parameters: Wavelength and pulse duration adjustments are vital for darker skin to minimize adverse effects.
- Professional Evaluation: Dermatologists with experience in laser procedures on darker skin are essential for evaluating skin type, melasma severity, and the most appropriate laser options.
Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) Therapy for Melasma: Is It Effective?
Following the examination of laser treatments for Melasma, another notable modality that merits discussion is Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) therapy.
This technique targets melasma lesions with high-intensity light pulses, which the darker-pigmented areas absorb.
It’s essential to distinguish IPL’s impact from other light treatments, as it specifically addresses the ultraviolet radiation-induced aspects of melasma and hyperpigmentation, which are particularly effective in sun-exposed areas.
While IPL can reduce the severity index of Melasma, its efficacy varies based on individual treatment of melasma, triggers and skin types.
Dermatologists often recommend combining IPL with topical agents to prevent hyperpigmentation recurrence, positioning it among the best melasma treatment options when customized to the patient’s specific condition.
How Can Diet and Lifestyle Affect Melasma?
Dietary choices influence the health of the skin, with certain nutrients potentially exacerbating or mitigating the expression of Melasma.
Preventative measures, such as the consistent application of high SPF sunscreen, play an essential role in shielding the skin from exacerbation due to UV exposure.
Additionally, stress and hormonal fluctuations are recognized as significant triggers that can intensify Melasma, necessitating a holistic approach to management that includes stress reduction techniques and hormonal balance.
The Impact of Diet on Skin Conditions
Several studies suggest that dietary choices greatly influence the development and severity of Melasma, a skin condition characterized by dark, discolored patches.
Understanding how diet impacts Melasma can help patients manage their condition more effectively. Here are key dietary considerations:
- Avoid Foods that Trigger Melasma: Certain foods known to worsen Melasma should be avoided. These include processed and sugary foods, exacerbating inflammation and pigmentation issues.
- Incorporate Vitamin C-rich Foods: Vitamin C can benefit melasma patients by reducing melanin production. Foods rich in this vitamin may help prevent Melasma and reduce its recurrence.
Balanced Diet for Hormonal Balance: Eating a balanced diet helps regulate hormones that may trigger Melasma, thereby managing its severity and area coverage.

Preventing Melasma with Proper SPF and Sunscreen Use
While dietary adjustments serve as a fundamental approach to managing Melasma, equally essential is the vigilant use of sun protection.
Preventing Melasma involves consistent sunscreen use, specifically, products containing high SPF and iron oxide, which not only protect against UV rays but also against visible light—a lesser-known factor exacerbating Melasma.
The outer layer of face skin, being highly susceptible to the signs of Melasma, requires robust shielding to prevent the condition from getting worse.
Causes of Melasma include genetic predispositions and environmental triggers, emphasizing the importance of a tailored approach to sunscreen application, concentrating on areas most affected.
Through diligent application, individuals can appreciably mitigate the risk of intensifying the pigmentation, thereby maintaining the aesthetic integrity of their skin.
Can Stress and Hormones Worsen Melasma?
Can stress and hormonal changes exacerbate Melasma? Indeed, both factors play significant roles in Melasma’s pathogenesis, often worsening the condition. Here’s how:
- Hormonal Fluctuations: Commonly known as “the mask of pregnancy,” Melasma due to hormonal shifts is prevalent during pregnancy or when using oral contraceptive pills.
- Stress: Emotional stress can disrupt hormonal balance, indirectly affecting skin pigmentation.
- Diagnosis Complexity: Diagnosing Melasma involves understanding that pigmentation is caused by these combined factors, necessitating a holistic approach to treatment and management.
What is the Role of a Dermatologist in Melasma Treatment?
A dermatologist plays a pivotal role in managing and treating Melasma itself, beginning with determining the appropriate timing for medical consultation.
They are adept at developing personalized treatment plans that consider the unique skin characteristics and health history of each patient.
Throughout treatment, dermatologists meticulously monitor the effectiveness of prescribed therapies, making necessary adjustments to optimize outcomes.
They may also evaluate the suitability of advanced treatments like Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) for individual cases.
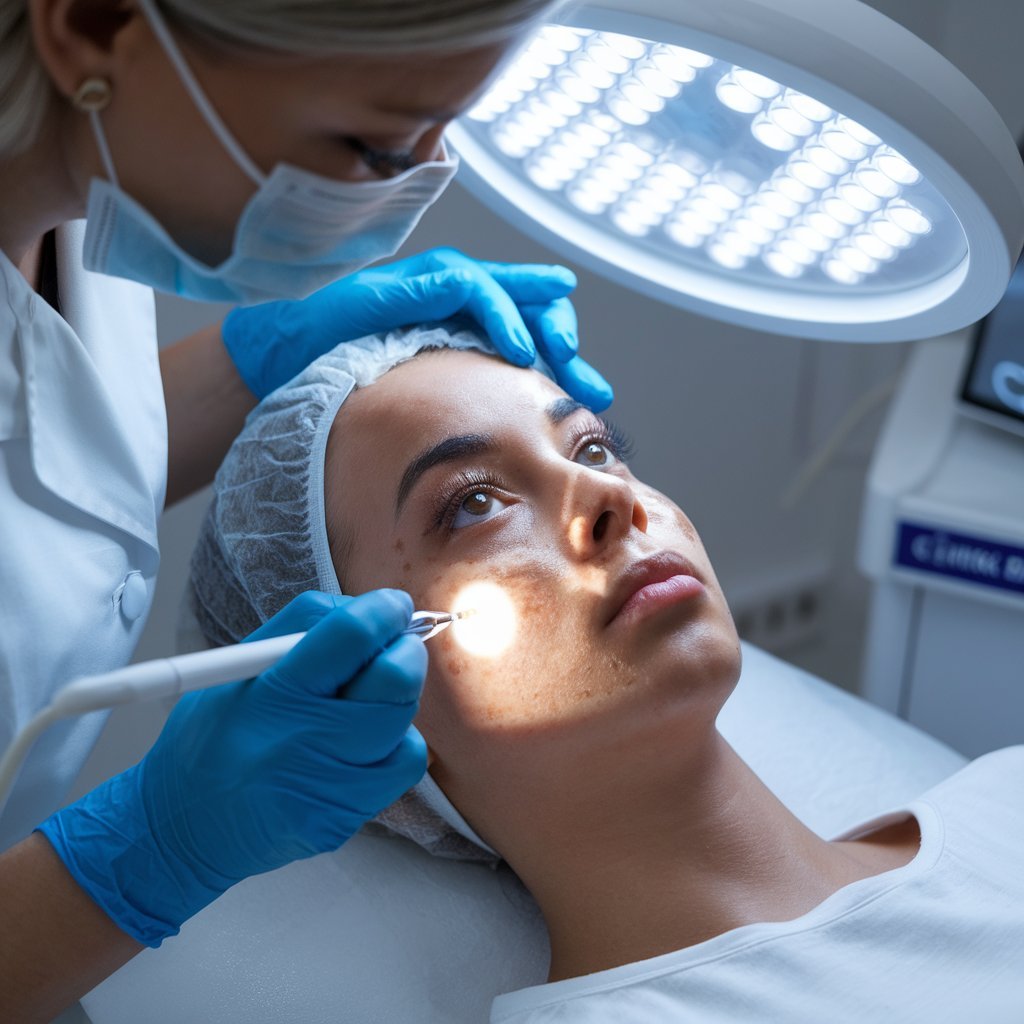
When to Consult a Dermatologist for Melasma
When addressing the complex and often persistent issue of Melasma, consulting a dermatologist is essential for an effective treatment strategy.
Dermatologists are pivotal in managing this condition, which is notoriously hard to treat. Here are key reasons to seek their expertise:
- Accurate Diagnosis: Using tools like a Wood’s lamp, dermatologists can assess how deeply Melasma affects the skin, influencing treatment choices.
- Advanced Treatments: Options include glycolic acid peels, types of laser treatments, and platelet-rich plasma, which are used to treat more persistent cases.
- Customized Care: Dermatologists determine the proper treatment based on individual skin type and melasma severity, ensuring each patient receives the most appropriate and effective care for their specific condition.
Developing a Personalized Treatment Plan
Developing a personalized treatment plan for Melasma involves a dermatologist’s in-depth understanding of the condition’s multifaceted nature. Melasma, sometimes called the “mask of pregnancy,” mainly affects women and presents as a coloration on the upper lip, cheeks, and forehead. Using a Wood’s lamp, dermatologists can determine the depth of pigmentation, which is vital for identifying whether it is epidermal, dermal, or mixed Melasma.
|
Tool/Technique |
Purpose |
|
Wood’s lamp |
Assesses depth of melasma pigmentation |
|
Soybean extract |
Inhibits pigmentation, lightens color caused by melasma |
|
Minimally invasive procedure |
Targets specific areas for best results |
|
Detailed history assessment |
Understands how melasma affects the individual |
|
Follow-up schedule |
Guarantees treatment effectiveness, adjusts as necessary |
The plan is tailored to achieve the best results, considering that melasma cannot be cured but managed.
Monitoring and Adjusting Treatments for Best Results
Monitoring and adjusting melasma treatments are vital roles undertaken by dermatologists to guarantee ideal outcomes for patients.
These specialists utilize a variety of tools and techniques to ascertain the treatment regimen remains effective and safe over time, particularly in persistent cases of Melasma.
- Assessment with Wood’s Lamp: This device helps dermatologists better visualize the depth of pigment changes, which is essential for tailoring treatment approaches.
- Observation of Other Sun-Exposed Areas: Monitoring these areas helps assess the effectiveness of sun protection measures in the treatment plan.
- Regular Follow-Up Appointments: Scheduled visits evaluate the treatment’s progress and necessary adjustments, confirming the response aligns with aesthetic goals and skin health.
Is There Any Treatment for Melasma Using Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP)?
In evolving melasma treatments, Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) has emerged as an intriguing option, prompting dermatologists to explore its efficacy and integration into treatment protocols. PRP therapy involves using a concentration of a patient’s platelets to accelerate injured tissue healing and regenerate skin. By injecting PRP into the affected areas, dermatologists aim to improve skin texture and reduce pigmentation by stimulating collagen production and enhancing skin rejuvenation.
|
Aspect |
Detail |
Significance |
|
Component |
Platelets-rich in growth factors |
Promotes tissue repair |
|
Method |
Injection directly into lesions |
Targets melanocytes |
|
Expected Outcome |
Improved skin texture, reduced pigmentation |
Enhances aesthetic appearance |
|
Research Status |
Emerging, with ongoing studies |
Promising but needs more evidence |
This table encapsulates the potential of PRP in melasma treatment, highlighting the clinical approach and ongoing research into its effectiveness.
Can Melasma be Prevented or Permanently Cured?
While Melasma cannot be permanently cured, understanding the limitations of current treatments is essential for managing expectations.
Preventative strategies, such as rigorous sun protection and avoidance of known triggers, play a pivotal role in mitigating the worsening of Melasma.
Furthermore, long-term maintenance involving topical agents and lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce the likelihood of recurrence, maintaining the skin’s aesthetic integrity.
Understanding the Limitations of Melasma Treatments
The short answer is no; Melasma cannot be completely prevented or permanently cured due to its complex etiology involving genetic factors, hormonal influences, and UV exposure.
However, understanding its limitations can guide effective management strategies:
- Genetic Predisposition: Individuals with a family history of Melasma are more likely to develop the condition, indicating a genetic component that cannot be altered.
- Hormonal Factors: Melasma often worsens with hormonal fluctuations such as those experienced during pregnancy or with contraceptive use, making complete prevention challenging.
- UV Exposure: While strict sun protection can minimize the severity of Melasma, it does not guarantee prevention or cure, as even minimal sun exposure can trigger pigmentation in susceptible individuals.
Strategies to Prevent Melasma from Getting Worse
Although Melasma cannot be prevented or cured permanently, adopting rigorous sun protection measures can significantly mitigate its progression. The skin’s exposure to UV rays intensifies the darkening of melasma patches, making sun avoidance and protection critical. Continuous application of broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF and wearing protective clothing are essential. Additionally, seeking shade during peak sunlight hours—typically 10 a.m. to 4 p.m.—further reduces exposure.
|
Strategy |
Details |
|
Sunscreen Application |
Use broad-spectrum, SPF 30+ |
|
Protective Clothing |
Hats, long sleeves, and sunglasses |
|
Time of Day |
Avoid sun exposure 10 a.m. – 4 p.m. |
|
Cosmetic Camouflage |
Use tinted sunscreens or foundations |
|
Lifestyle Adjustments |
Limit outdoor activities during peak hours |
These measures not only prevent the condition from worsening but also contribute to the skin’s overall health.
Long-term Maintenance to Reduce Recurrence
Despite diligent prevention efforts, the question remains regarding the potential for long-term management and the likelihood of permanently curing Melasma. While Melasma can be notoriously persistent, specific strategies may help maintain its reduction:
- Continuous Sun Protection: Daily use of broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher is vital, as UV exposure is a primary trigger for Melasma.
- Regular Dermatological Treatments: Incorporating chemical peels, laser therapy, or microdermabrasion treatments can help manage pigmentation when done under professional guidance.
- Consistent Topical Regimens: Using prescribed depigmenting agents like hydroquinone, azelaic acid, or tranexamic acid continuously or as maintenance therapy can prevent recurrence.
Adherence to these strategies, coupled with regular monitoring by a dermatologist, is essential for managing melasma long-term.
Conclusion
In summary, while Melasma presents a complex challenge, effective management is achievable through a multifaceted approach. Dermatologist-recommended treatments are essential, including topical agents, laser therapies, and chemical peels. Additionally, lifestyle modifications and dietary adjustments play significant roles in mitigation. Though prevention and permanent cure remain elusive, ongoing research and individualized treatment strategies offer hope in managing this condition, emphasizing the importance of professional dermatological guidance and patient adherence to prescribed regimens.

Dr. Sheena Majella is a certified dermatologist and the leading skin specialist at Tune Aesthetics. With a deep passion for skin health and beauty, she combines medical expertise with advanced aesthetic treatments to help clients look and feel their best.