Different Types of Stretch Marks and Their Common Risk Factors
- Home
- Mole, Wart & Skin Tag Removal
- types of stretch marks

Stretch marks, or striae, encompass types like striae rubrae, which are red or purple, and striae albae, which fade to white with time. Striae gravidarum relate specifically to pregnancy. Common risk factors include rapid skin stretching during puberty, pregnancy, and weight fluctuations. Hormonal changes further exacerbate collagen and elastin deficiencies, pivotal in skin elasticity. Various stretch mark treatments and prevention strategies exist to combat these marks, with additional insights on their permanence and care readily accessible.
Key Takeaways
- Striae Rubrae is early-stage stretch marks with a red or purple hue, often due to rapid skin stretching.
- Striae Albae are mature stretch marks, appearing as white or silver lines, resulting from long-term skin changes.
- Striae Gravidarum is pregnancy-related stretch marks caused by skin stretching and hormonal changes.
- Rapid weight gain and hormonal fluctuations are common risk factors that disrupt skin elasticity, leading to stretch marks.
- Collagen and elastin deficiencies weaken skin structure, increasing susceptibility to stretch marks during physiological changes.
Exploring the Various Types of Stretch Marks
Stretch marks, or striae, manifest in various forms that can be clinically categorized based on their appearance and etiology.
Striae rubrae represents the acute phase, characterized by their red or purple hue, while striae albae are the result of chronic maturation, appearing as hypopigmented, atrophic lesions.
Additionally, striae gravidarum is a specific variant associated with pregnancy, often resulting from rapid dermal stretching and hormonal changes.
Understanding Striae Rubrae: The Early Stage
Striae rubrae, the initial stage of stretch marks, are characterized by their red or purplish hue and occur due to the rapid stretching of the skin. This early stage is clinically significant as it represents the period when intervention may be most effective.
The appearance of stretch marks at this stage is attributed to the disruption of skin elasticity, involving the breakdown of collagen and elastin fibers. Hormonal changes, particularly during pregnancy, exacerbate this process, leading to pronounced red or purple discoloration.
The compromised dermal structure results from the skin’s inability to withstand rapid stretching. Understanding the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying striae rubrae can guide treatment strategies aimed at preserving collagen integrity and enhancing skin resilience during this vulnerable period.
Exploring Striae Albae: Mature Stretch Marks
Following the initial phase of striae rubrae, the progression to striae albae marks a significant morphological change in the appearance of stretch marks. These mature stretch marks, a common skin concern, present as hypopigmented lines that contrast with the surrounding skin tone. The texture and color of stretch marks evolve due to alterations in collagen and elastin. While striae albae are permanent, treatments can help improve the appearance and reduce the appearance of stretch marks. Various therapeutic options, including laser therapies, target the remodeling of collagen to enhance skin texture and color.
Property | Striae Rubrae | Striae Albae |
Color | Red/Purple | White/Silver |
Collagen Structure | Disorganized | Stabilized |
Skin Tone Contrast | High | Low |
Treatment Options | Topical, Laser | Laser, Microdermabrasion |
Improvement Focus | Vascularization | Collagen Remodeling |
Identifying Striae Gravidarum: Commonly Known As Pregnancy Stretch Marks
Pregnancy, a transformative period in a woman’s life, often leads to the development of striae gravidarum, commonly referred to as pregnancy stretch marks.
These dermal lesions typically manifest on the abdomen as the skin stretches to accommodate fetal growth. Stretch marks occur due to the rapid weight gain and pregnancy, causing the dermal layer of skin to tear when elasticity is exceeded.
The common causes include hormonal changes and mechanical stress on the skin. While striae gravidarum is a natural consequence of pregnancy, interventions to reduce the appearance focus on maintaining skin elasticity through topical treatments and hydrating agents.
Evidence suggests that early intervention may minimize these marks, although complete prevention remains challenging due to intrinsic skin characteristics.
What are the Common Causes of Stretch Marks?
Stretch marks, or striae, primarily occur due to disruptions in the dermal matrix, particularly affecting collagen and elastin fibers.
Rapid weight gain and hormonal changes during puberty can lead to increased skin tension, thereby predisposing individuals to these dermal tears.
Additionally, the physiological changes and mechanical stretching of the skin during pregnancy greatly contribute to the development of stretch marks in expectant mothers.
The Importance of Collagen and Elastin in Skin Health
Collagen and elastin are fundamental proteins that contribute greatly to the skin’s structural integrity and elasticity.
When collagen production is disrupted, it affects the skin’s ability to withstand the stretching of the skin, often leading to different types of stretch marks.
Elastin, essential for skin elasticity, can degrade over time, further exacerbating the risk factors for these dermal lesions.
The following highlights the impact of collagen and elastin on stretch marks:
- Collagen Deficiency: Insufficient collagen production weakens the layer of the skin, making it more susceptible to tears.
- Elastin Degradation: Reduced elastin diminishes the skin’s resilience, increasing the likelihood of stretch marks.
- Compromised Structural Integrity: Combined deficits in collagen and elastin can severely impair the skin’s structural integrity.
Addressing these factors may improve skin elasticity and reduce the cause of stretch marks.
How Weight Gain and Puberty Affect Stretch Marks
Significant physiological changes, such as those experienced during weight gain and puberty, are primary contributors to the development of stretch marks.
During rapid weight gain, the skin undergoes excessive stretching, disrupting collagen and elastin fibers. This mechanical stress may result in the formation of striae, commonly referred to as stretch marks, which often appear on the abdomen.
Adolescents undergoing puberty experience a similar phenomenon, as rapid growth spurts can lead to the development of these lines on the skin.
The severity of stretch marks is influenced by genetic predisposition and the rate of skin expansion.
Clinically, the appearance of stretch marks is characterized by red or purple lines that gradually fade to a lighter tone, indicating dermal damage and subsequent healing processes.
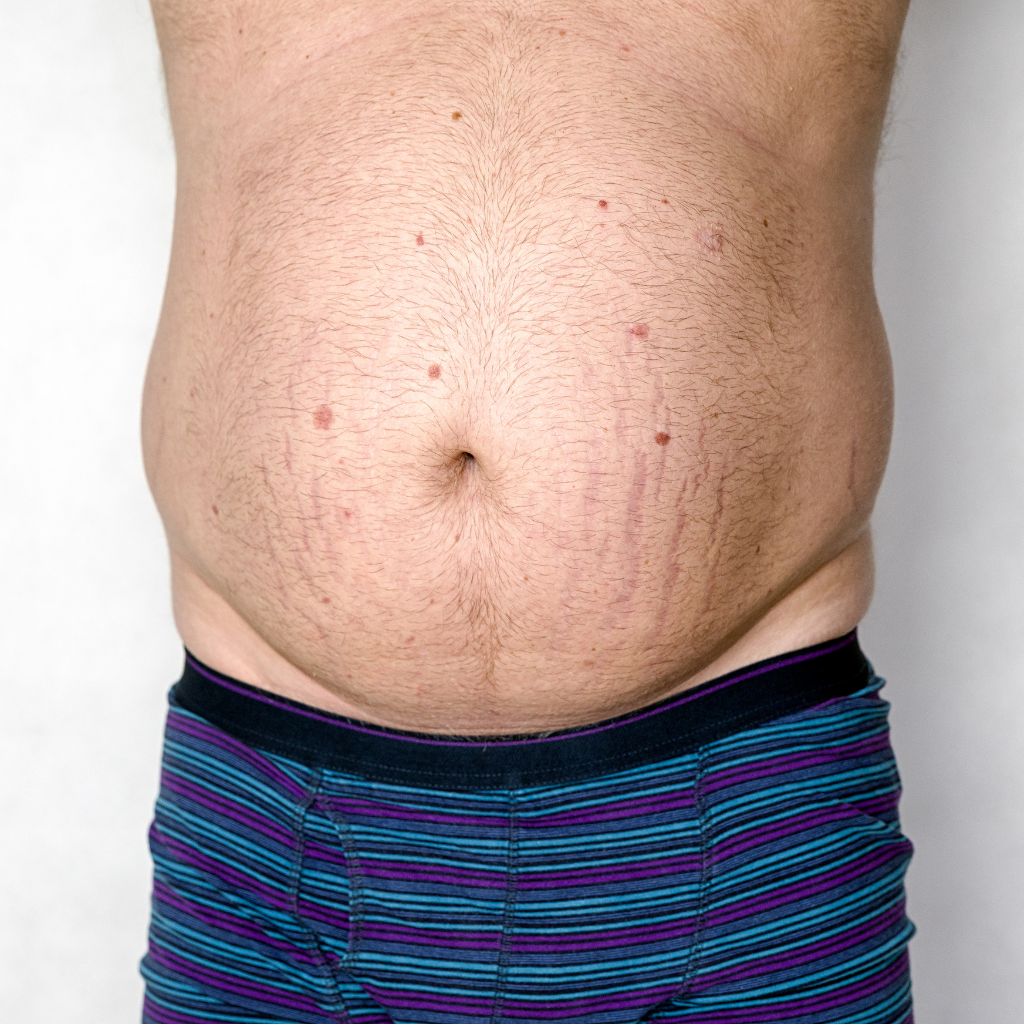
Impact of Pregnancy on Stretch Mark Development
During pregnancy, the physiological changes in a woman’s body greatly increase the likelihood of stretch mark formation.
As pregnancy is a common cause, specific types of stretch marks during pregnancy, commonly known as striae gravidarum, occur when the skin is stretched rapidly. The initial stage of stretch marks appears as red or purple lines that later shift to white or silver marks. These marks appear mainly on the abdomen, thighs, and breasts.
The following list highlights key factors contributing to their development:
- Rapid Weight Gain: Excessive stretching of the skin compromises its integrity.
- Hormonal Changes: Fluctuations may hinder collagen synthesis, weakening the dermal structure.
- Genetic Predisposition: Family history may influence susceptibility.
Preventive strategies include interventions to stimulate collagen production to enhance skin elasticity.
Can You Prevent Stretch Marks?
Preventing stretch marks involves implementing strategies aimed at enhancing skin elasticity and mitigating specific risk factors, particularly during pregnancy.
Evidence suggests that topical formulations containing hyaluronic acid or centella asiatica extract may improve skin hydration and elasticity, potentially reducing the likelihood of stretch mark development.
Additionally, maintaining a healthy weight and a balanced diet rich in vitamins C and E can further support skin resilience and decrease the incidence of pregnancy-related stretch marks.
Strategies to Improve Skin Elasticity
Enhancing skin elasticity is a pivotal strategy that potentially minimizes the likelihood of developing stretch marks.
Clinical evidence suggests that certain topical treatments can improve the appearance of stretch marks and help reduce their formation.
Key components include:
- Cocoa Butter and Vitamin E: These are common skin emollients that may aid in increasing skin hydration, thereby potentially preventing stretch marks.
- Creams Containing Ingredients Like Retinoids: Retinoids are known to enhance skin cell turnover and collagen synthesis, which can improve skin elasticity.
- Hyaluronic Acid-Based Creams: These are effective in maintaining skin moisture levels, promoting elasticity, and reducing the risk of stretch mark formation.
Adopting these strategies can be integral in maintaining skin resilience and elasticity, thereby supporting efforts to prevent stretch marks.
How to Reduce the Risk Factors of Pregnancy Stretch Marks
Pregnancy stretch marks present a common dermatological concern, with their formation primarily influenced by rapid skin stretching and hormonal changes.
Understanding stretch marks begins with recognizing that various types of stretch marks may appear, each with unique characteristics.
To reduce the risk, individuals should focus on maintaining ideal skin hydration and nutrition, as these factors can influence skin elasticity.
Although no definitive treatment options guarantee prevention, topical emollients and creams may help reduce stretch marks and the appearance of emerging marks.
Stretch marks can occur despite preventive efforts; however, they often fade over time.
Managing stretch marks involves early intervention and consistent skin care strategies.
While one cannot completely get rid of stretch marks, strategic approaches may assist in minimizing their visibility and supporting skin integrity.
How to Treat Stretch Marks?
The treatment of stretch marks involves a range of evidence-based interventions aimed at reducing their appearance by boosting collagen production to enhance skin elasticity.
Clinical options such as laser therapy, microdermabrasion, and topical retinoids have demonstrated varying degrees of efficacy in improving stretch mark visibility.
While complete eradication of stretch marks is not typically feasible, these treatments can considerably ameliorate their appearance and improve overall skin texture.
Effective Treatment Options for Reducing Stretch Marks
Addressing the challenge of stretch marks involves exploring a variety of evidence-based treatment options that can effectively reduce their appearance.
Stretch marks are common and typically appear due to rapid skin stretching. Different types of stretch marks may necessitate varied approaches to treatment. Evidence suggests that new stretch marks respond more favorably to interventions.
Effective treatment options include:
- Topical Retinoids: These compounds can promote cell turnover, making stretch marks less visible.
- Laser Therapy: This method targets affected areas, stimulating dermal repair and reducing the appearance of stretch marks.
- Microdermabrasion: This technique exfoliates the skin surface, potentially enhancing texture and decreasing the prominence of stretch marks.
Each type of stretch mark requires tailored interventions, emphasizing the importance of selecting the appropriate method to reduce stretch marks considerably.
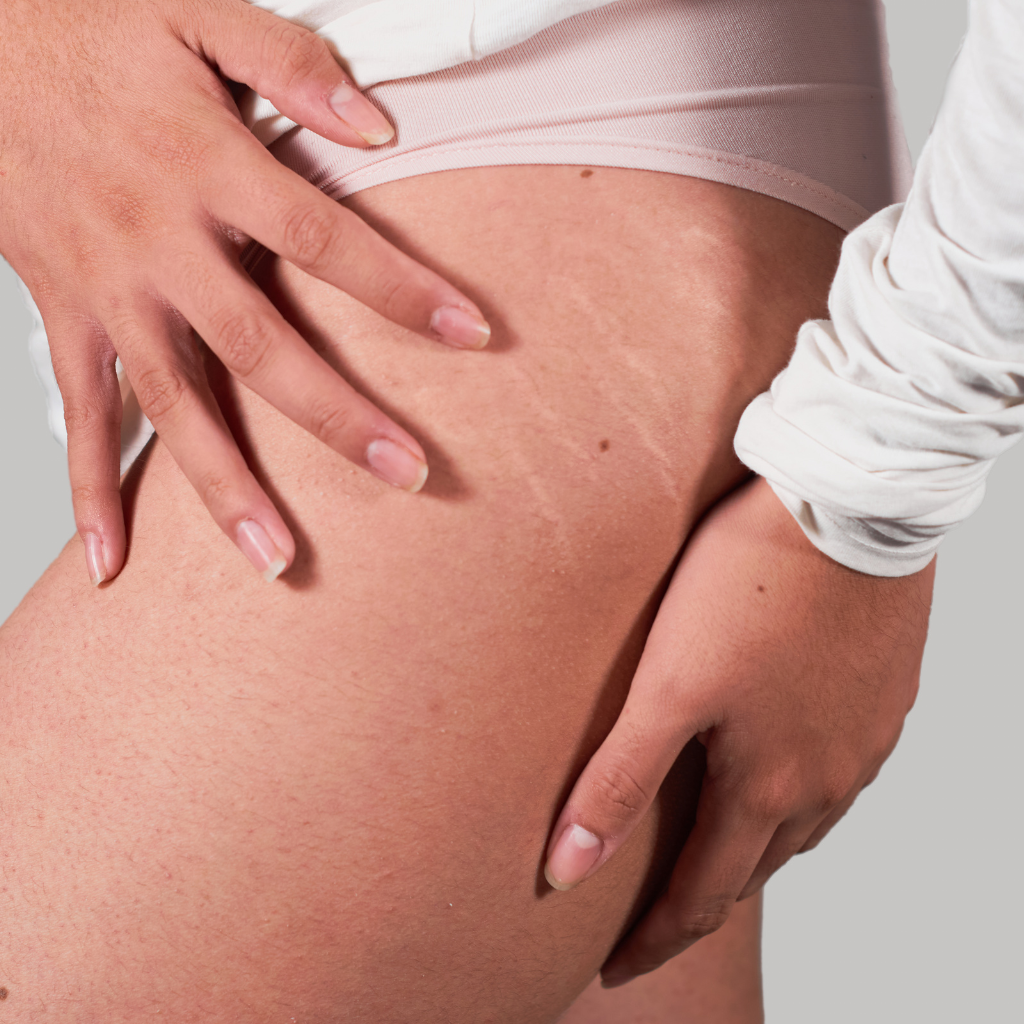

How to Stimulate Collagen Production for Better Results
A critical aspect of treating stretch marks involves stimulating collagen production to enhance skin elasticity and repair. Collagen synthesis is essential for dermal repair, and various methods can be employed to promote this process. Topical treatments containing retinoids and vitamin C have shown efficacy in improving skin elasticity and stretch marks by stimulating collagen production. Incorporating these into a consistent skin care routine is vital. Maintaining skin hydration supports collagen synthesis and overall skin health.
Method | Key Component | Function |
Topical Treatments | Retinoids | Stimulate collagen production |
Nutritional Support | Vitamin C | Enhance collagen synthesis |
Hydration | Water | Improve skin elasticity |
Skin Care Routine | Consistency | Support dermal repair |
Clinical Procedures | Microneedling | Boost collagen production |
Is It Possible to Completely Get Rid of Stretch Marks?
Can stretch marks be eradicated? Current clinical evidence suggests that stretch marks are permanent.
However, various treatments may help reduce stretch marks’ appearance or alter the color of stretch marks over time. While complete elimination is unlikely, options for effective stretch‑mark removal focus on improving texture and tone, making marks less noticeable.
Consider the following interventions:
- Laser Therapy: It targets the discoloration and may help reduce stretch marks’ visibility, especially during the early stages when stretch marks begin.
- Topical Retinoids: These compounds can promote collagen production, potentially improving the skin’s texture.
- Microdermabrasion: This technique may improve the skin’s surface by exfoliating and promoting new cell growth.
While complete removal is elusive, these methods offer potential pathways for improvement.
Are Stretch Marks Permanent?
The permanence of stretch marks is contingent upon their morphological evolution over time, changing from red or purple hues to more attenuated, silvery lines.
Clinical evidence suggests that while stretch marks do not completely vanish, their visibility can diminish as the dermis undergoes remodeling.
Individual skin characteristics and external interventions may influence this fading process.
Understanding the Appearance of Stretch Marks Over Time
Though often considered a cosmetic concern, stretch marks, or striae, undergo a distinct transformation over time. The aging of stretch marks involves several stages, each reflecting the body’s response to dermal tearing and treatments that can help reduce the appearance of these marks.
Initially, stretch marks can appear as red or purple lines, particularly on the abdomen. Over time, they may fade to a lighter hue, depending on the type of stretch and darker complexion skin types. Understanding the different types is essential, as stretch marks are caused by rapid skin stretching.
- Emotional Impact: The initial vivid appearance may evoke distress.
- Physical Transformation: Striae gradually lighten, signifying healing.
- Perception Shift: As stretch marks age, acceptance may increase.
Clinically, the stage of stretch marks dictates management approaches and patient expectations.
Do Stretch Marks Fade with Time?
As stretch marks evolve through various stages, their permanence becomes a focal point of consideration.
Stretch marks, clinically known as striae, are dermal scars that manifest differently depending on several factors, including type and location. Commonly appearing on the thigh and buttocks, these marks often result from rapid skin stretching, such as those experienced during pregnancy.
It is essential to know that stretch marks are not entirely permanent; they tend to fade over time. The initial red or purple hue typically lightens to a silvery-white, though the degree of fading varies among individuals.
Evidence suggests that both intrinsic factors, like genetics, and extrinsic factors, such as the degree of skin tension, influence the fading process. Consequently, while not entirely vanishing, stretch marks become less conspicuous.
Conclusion
To sum up, stretch marks, or striae, manifest in various forms, including striae rubrae and striae albae, and are often found on the abdomen. Stretch marks typically result from factors such as hormonal changes, rapid growth, or weight fluctuations. While genetic predisposition plays a significant role, preventative measures like maintaining skin hydration and gradual weight management may mitigate their development. Treatment options, ranging from topical retinoids to laser therapy, offer varying efficacy. However, stretch marks often remain a permanent, albeit less pronounced, dermatological feature.

Highly skilled cosmetologist at Tune Clinical Aesthetics, specializing in advanced skin and hair treatments.