What is Acne Marks on Face? Understand Type of Acne, and How to Get Rid of Acne Scars
- Home
- Acne Scars
- What is Acne Marks on Face?

Acne marks on the face can refer to post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) or to true acne scars. Scars form when inflammation damages deeper skin layers and healing disrupts collagen. Common scar types include atrophic (ice pick, boxcar, rolling) and raised hypertrophic and keloid scars. Severe, nodular or cystic acne is more likely to scar. Effective options range from topical retinoids to procedures like laser therapy, chemical peels, microneedling, subcision and fillers—selected by scar type and severity. Early intervention and consulting a skin specialist can improve outcomes and help prevent new marks. Explore further to learn proven ways of preventing and managing acne scars effectively.
What Are the Different Types of Acne Scars?
Acne scars are classified by appearance and healing response. Atrophic scars are depressions from collagen loss, while hypertrophic and keloid scars are raised due to excess collagen.
Ice pick scars are narrow and deep; boxcar scars are broader with sharper edges; rolling scars create wave-like depressions. Identifying the type helps choose treatments (e.g., TCA CROSS for ice pick; microneedling/fillers for boxcar; subcision for rolling).
What Are Atrophic Scars and How Do They Form?
Atrophic scars develop when inflammation disrupts collagen and the skin fails to regenerate fully, leaving a sunken area. Deep acne can damage support structures and cause the outer layer to collapse into the dermis.
Standard, evidence-based options stimulate collagen and remodel texture. Summary:
Type of Atrophic Scar | Recommended Treatments |
Ice Pick | TCA CROSS, Punch excision, Laser therapy, Chemical peels |
Boxcar | Microneedling, Dermal fillers, Fractional laser, Subcision |
Rolling | Subcision, Radiofrequency microneedling, Fractional laser |
Matching treatment to scar subtype improves outcomes and overall skin health.
Exploring Hypertrophic and Keloid Scars
These raised scars result from excess collagen during healing. Hypertrophic scars remain within the original wound; keloids extend beyond it and may continue thickening.
Helpful options include silicone sheeting, corticosteroid injections, cryotherapy, vascular/ablative lasers, or surgery (with measures to lower recurrence risk).
How Do Ice Pick and Boxcar Scars Differ?
Ice pick scars are deep, narrow pits (often on thinner skin like the cheeks) and may respond to TCA CROSS or punch techniques. Boxcar scars are wider with defined edges, commonly on lower cheeks/jaw; microneedling, fractional lasers, dermal fillers or microdermabrasion can help by boosting collagen and smoothing the surface.
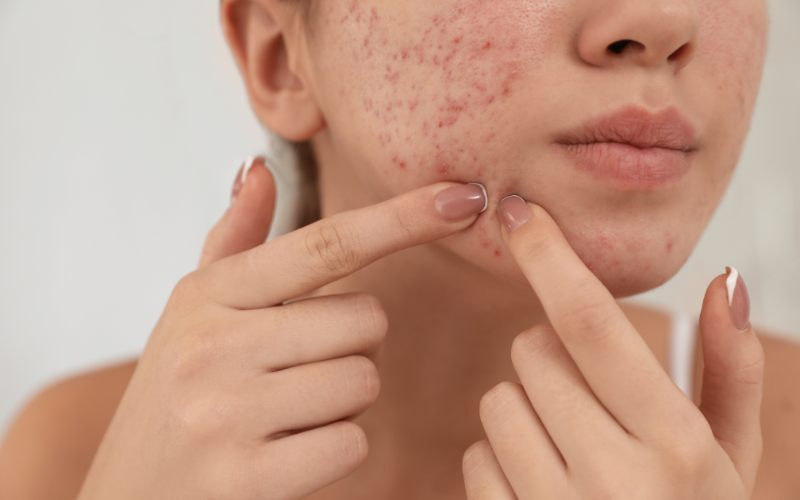

What Causes Acne Scarring?
Inflammation damages collagen and supporting tissue. Picking or squeezing interrupts the natural healing process and pushes debris deeper, raising scar risk. Severe nodular or cystic acne has a higher chance of leaving permanent texture changes.
Does Squeezing Your Acne Lead to Scars?
Squeezing or picking acne lesions can rupture the follicle wall, spread bacteria/inflammation, and deepen injury—triggering scar-forming collagen fibres. Avoid manual extraction unless guided by a professional.
How Severe Acne Can Leave Marks
Deep nodules/cysts disrupt the dermis; new collagen may form unevenly, causing pits or raised tissue. You may also see post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (dark spots) that mimic scars but usually fade with time and sun protection.
- Inflammation weakens skin architecture.
- Collagen damage causes uneven texture.
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH) = dark marks, not scars.
- Pitting can follow widespread inflammation
- Raised scars can form when extra tissue builds during healing.
Are Certain Types of Acne More Likely to Scar?
Yes—nodular and cystic acne, delayed treatment, and frequent picking raise risk. Some skin tones are more prone to noticeable discolouration (PIH). Early, effective acne control helps prevent both acne scars and acne marks.
How Can You Treat Acne Scars Effectively?
Successful plans combine skincare (SPF, retinoids) with targeted procedures. Choice depends on scar type, depth, and skin tone.
What Treatments for Acne Scars Are Available?
- Topical Retinoids to boost turnover and collagen.
- Chemical Peels (glycolic/salicylic/TCA) for texture and discolouration.
- Laser Therapy (ablative/non-ablative; fractional) to resurface and stimulate collagen.
- Microneedling or RF microneedling for atrophic scars.
- Fillers (e.g., hyaluronic acid) to lift depressed scars; sometimes combined with subcision.
Consult a dermatologist to tailor modality, sequence, and downtime to your skin.
How Can Treatments Help Reduce the Appearance of Scars?
Laser therapy and microdermabrasion resurface the top layers; dermal fillers and subcision address deeper pits. Chemical peels improve texture and lighten discolouration, while retinoids and vitamin C support cell turnover and tone.
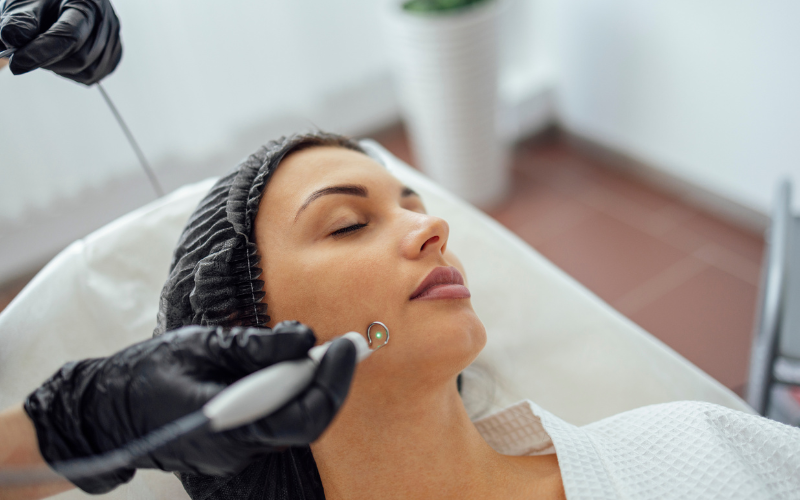
How to Prevent Acne and Minimise Scarring?
Preventing breakouts and treating early reduces the chance of acne marks on the face becoming scars.
What Are the Best Practices to Prevent Acne?
- Consistent skincare: gentle cleansers; non-comedogenic products.
- Daily SPF to prevent PIH and protect healing skin.
- Balanced diet: moderate high-GI foods and some dairy if they trigger you.
- Hands off: avoid picking to prevent worsening scars.
- Sleep & stress: good sleep and stress control help reduce flares.
When Should You See a Dermatologist for Acne Scarring?
Seek help if scars/marks persist, new breakouts keep appearing, or you’re unsure which treatment for acne scars suits your skin.
Why It’s Best to Talk to a Professional
- Expert diagnosis of scar types (boxcar, rolling, ice pick, hypertrophic/keloid).
- Tailored treatments: peels, lasers, microneedling, subcision, fillers.
- Prevention strategies to stop new scars.
- Advanced options are not available OTC.
- Holistic care that considers tone, sensitivity, and downtime.
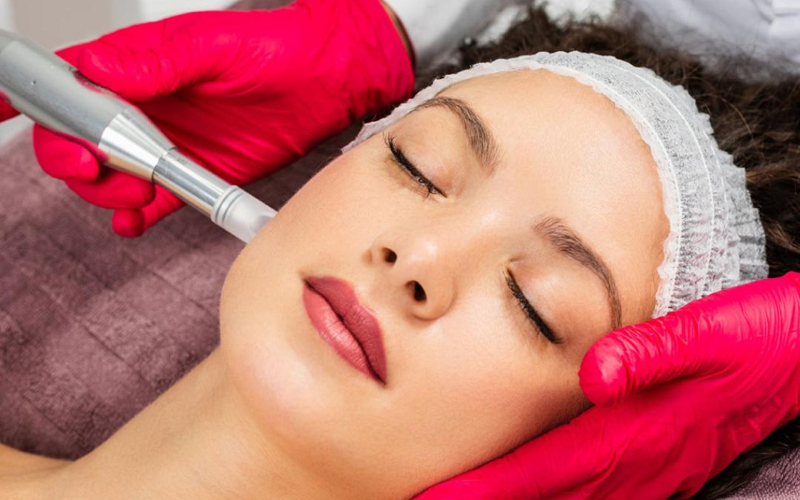
What Can a Dermatologist Do to Help Reduce Acne Scars?
They may use fractional laser treatments, chemical peels, filler injections, microneedling/RF, subcision, or TCA CROSS for precise ice-pick work—often in a staged plan to rebuild collagen and renew skin. In specific cases (e.g., postpartum changes), early care can prevent worsening marks; see our guide to postpartum acne.

Prevention & Healing FAQs
“Acne marks” vs. “acne scars”—what’s the difference?
People often ask about the difference between acne scars and acne marks. “Marks” usually refer to PIH (brown spots) or post-inflammatory erythema (pink/red spots). These are flat and typically fade. “Scars” change skin texture—pitted (atrophic) or raised (hypertrophic/keloid)—and may be permanent without treatment. If you’re wondering what pimple marks are called, they are PIH.
How to see acne scars (self-check)
Stand under side-lighting and look for texture changes (shadows/waves). This helps distinguish true scars from flat spots. This addresses the query of how to see acne scars and what acne scars look like.
How to know if acne scars are healing or fading
PIH usually fades over months with sunscreen/actives; erythema lightens as inflammation settles. Textural scars “heal” by remodelling after treatments (firmer feel, softer edges). This covers how to know acne scars are healing and how to know acne scars are fading.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between acne scars and acne marks helps set expectations. With targeted treatments and prevention, most people can soften texture and fade discolouration. If you’re asking what acne marks are or what acne marks on the face, think of PIH vs. true scars—then treat accordingly.




Деятельность в области недропользования — это совокупность процессов, связанный с изучением и использованием недр.
Оно включает разведку природных ресурсов и их промышленное освоение.
Недропользование регулируется законодательством, направленными на охрану окружающей среды.
Грамотный подход в недропользовании помогает сохранять ресурсы.
оэрн
Недропользование — это совокупность процессов, связанный с изучением и использованием недр.
Оно включает добычу минерального сырья и их дальнейшую переработку.
Данная сфера регулируется установленными правилами, направленными на сохранение природного баланса.
Грамотный подход в недропользовании помогает сохранять ресурсы.
оэрн
Dressing stylish creates a positive first impression.
Your outfit speaks volumes before you actually speak a single word.
It boosts your own confidence and mood significantly.
Your polished appearance signals professionalism in the office.
https://s1.luxepodium.com/7wa9AYYY0yFT/
Fashionable clothing allow you to showcase your unique identity.
Others often judge well-dressed people as more capable and trustworthy.
Therefore, putting effort in your wardrobe is an investment in your personal brand.